Lewy Body Measurement
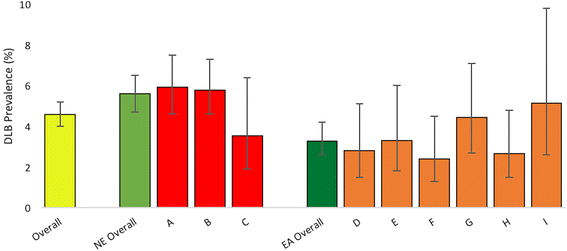
Dementia with lewy bodies dlb is a common neurodegenerative dementia in older people. Dementia with lewy bodies dlb is a complex multisymptom disorder. Indeed elevated levels of csf total tau considered a marker of axonal neuronal damage have been confirmed in cases with a definite diagnosis of ad lewy body variant of ad as well as dlb alone see. Lewy body diseases lbds are the result of abnormal accumulation of the synaptic protein alpha synuclein and include pd parkinsons disease dementia pdd and dlb. Cognitive impairment is common among pd patients and the prevalence of dementia in pd is approximately 30 to 40 increasing to 80 after 20 years goetz et al 2008. Collectively lewy body dementias represent the second most common neurodegenerative cause of dementia in the elderly walker et al 2015 with fluctuating cognition a core clinical feature in the diagnostic criteria for dlb since first being introduced in 1992 mckeith et al 1992 2017.
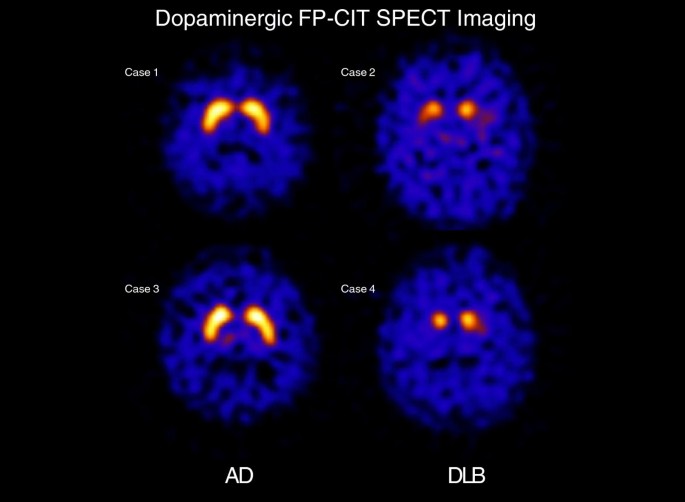
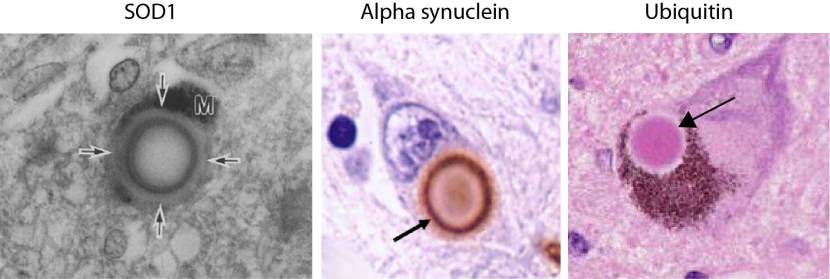
Dementia with lewy bodies dlb is the second most common type of degenerative dementia accounting for approximately 42 of all diagnosed dementia in the community and up to 75 of those in secondary care lewy body protein was first discovered by a german scientist friederich h. When making decisions regarding the treatment of dlb the patients quality of life qol should always be the main consideration. Table 3 thus reflecting the described impairment in axonal transport and axonal loss reviewed in underlying the development of both ad and lb pathologies. Lewy bodies are spherical intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies composed of abnormally phosphorylated neurofilament proteins aggregated with ubiquitin and α synuclein4 found in cortical and subcortical regions in dlb42 lewy body formation and neuronal loss in the brainstem nuclei particularly the substantia nigra leads to the movement disorder seen in dlb4 α synuclein has not been linked. To our knowledge this is the first review article focusing on the qol in dlb patients. Here we examine the literature for the evidence behind imaging modalities that could assist in making the diagnosis.
1 2 lewy bodies are the pathological hallmark of parkinsons disease but in this disease lewy bodies appear almost exclusively in the. The concept of dementia with lewy bodies dlb was first proposed in a case report by a japanese psychiatrist dr. Apathy in lewy body disorders is a common cause of disability and caregiver burden. 1 two years later based on their neuropathological findings from three autopsied cases kosaka 2 reported the characteristic distribution of lewy bodies in cerebral cortices in the subjects with the later so called diffuse lewy body disease dlbd. Kenji kosaka in 1976. Lewy in the early 1900s while doing research on parkinsons disease.
Hely et al 2008. In the 19 pd studies there were five different scales used to measure apathy with the exception of an rct published in 1961 which used a clinical interview to assess apathy. 1 2 the name dlb is derived from the pathology of the disorder in which there is widespread appearance of lewy bodies in the cerebral cortex and in the basal ganglia. Dementia of lewy body dlb type is the second commonest degenerative cause of dementia. Measurement of apathy. However the clinical features particularly cognitive fluctuations and rapid eye movement sleep disorder are often hard to elicit leading to difficulty in making the diagnosis clinically.
We searched the pubmed database using the keywords x201cquality of lifex201d.
Random Post
- hayley williams body measurement
- dimensions body piercing
- us body measurement chart
- ezra miller body measurement
- get body measurement
- morgan ortagus body measurement
- body measurement stickers
- body fat measurement glasgow
- salman khan body measurements
- esther acebo body measurement
- body fat measurement dublin
- temperature sensor for body temperature measurement
- city body measurement
- park shin hye body measurement
- body temperature measurement instruments
- bhoomika dash body measurement
- navy body measurement standards
- irina shayk body measurement
- list of body measurement
- bhojpuri actress body measurements
- bra size b
- mohit raina body measurement
- jensen ackles body measurement
- jeep body measurements
- dhruv vikram body measurement
- nikhil siddharth body measurements
- inaccurate body fat measurement
- liana liberato body measurement
- body measurement excel
- aparna dixit body measurements
- triumph bra measurement guide
- bruno mars body measurements
- body muscle measurement chart
- simeon panda body measurement
- bra size vs bust measurement
- beren saat body measurement
- jordyn woods body measurement
- qei body measurement
- tiwa savage body measurement
- chitharesh natesan body measurement
- sheela kaur body measurement
- mia fizz body measurements
- body measurement kate wright
- alexey lesukov body measurement
- meagan good body measurement
- perfect body measurement ratio
- larry scott body measurements
- niveda thomas body measurement
- what stores do bra measurements
- twice momo body measurement