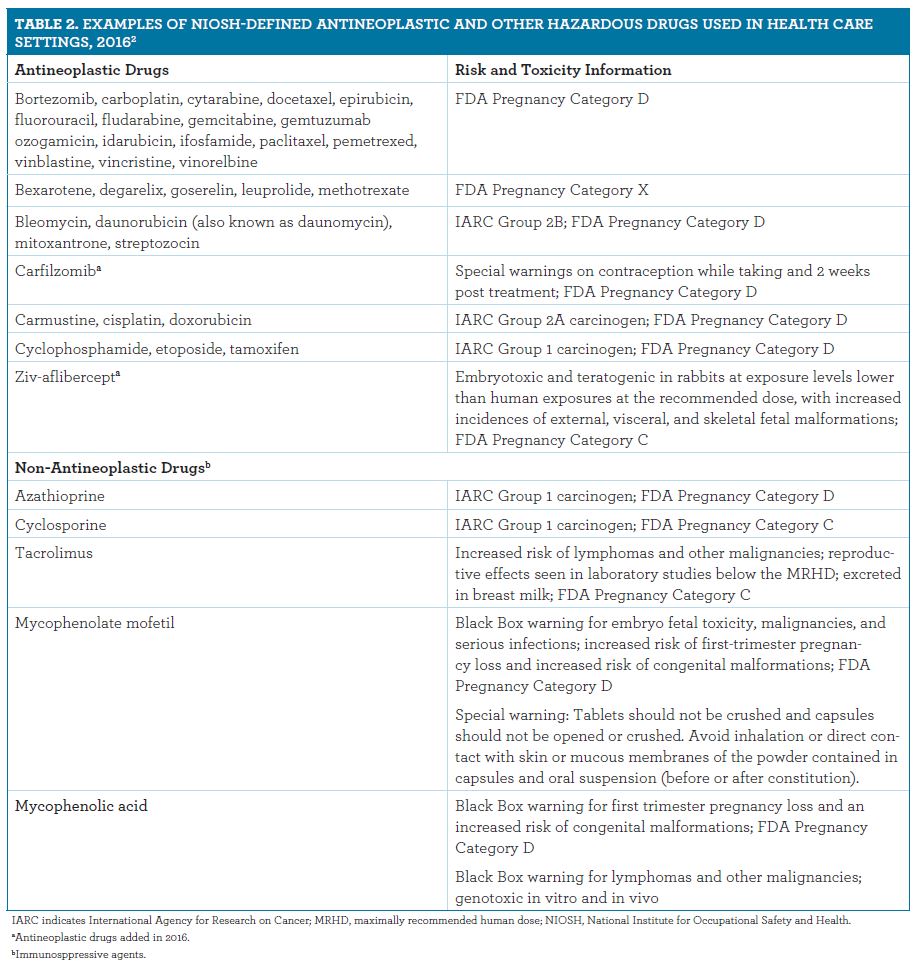
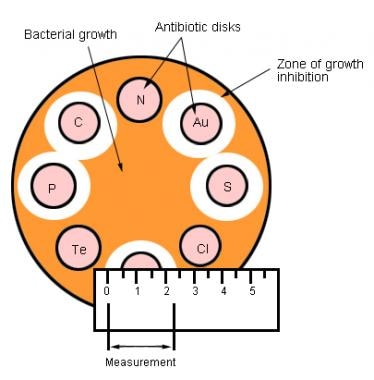
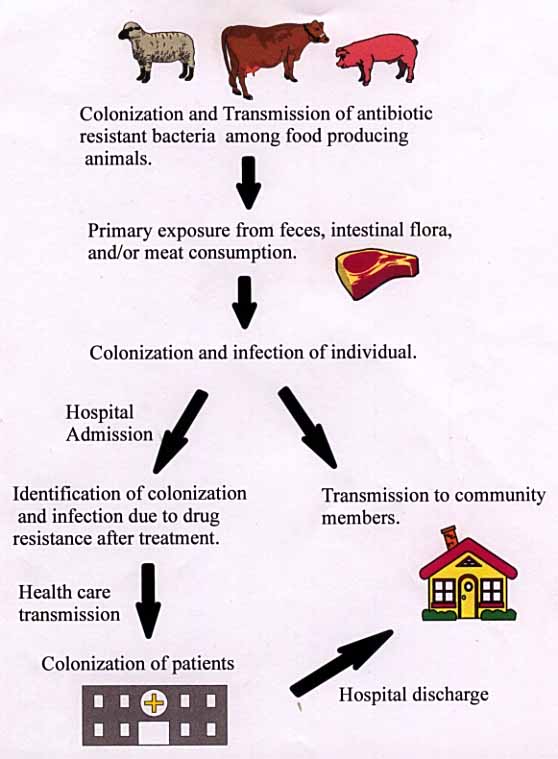
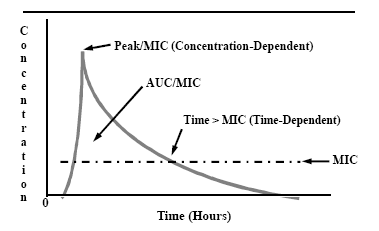
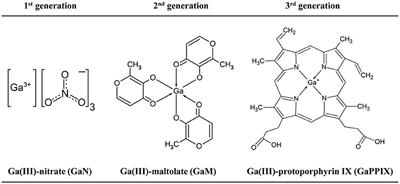
Measurement Of Antimicrobial Agents Levels In Body Fluids
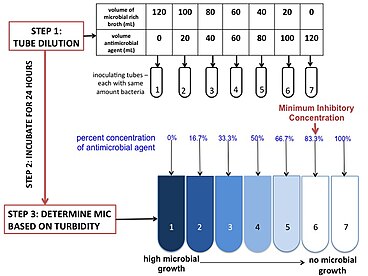
In contrast dilution methods allow determination of the minimal inhibitory concentration of an agent which can be correlated with blood urine and other body fluid levels of the antimicrobial agent. Gonorrheae strains with clinical response to penicillin and its blood levels. Concentration of antibacterial agents in interstitial tissue fluid. Pharmatokinetic properties of antimicrobial drugs determine the dosage the dosing frequency and. Correlation of in vitro resistance ofn. Pmc free article georgopoulos a.
Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy. The fact that the native structure of fluconazole contains two fluorine atoms makes it an ideal candidate for radiolabeling with 18f. Indian journal of medical. Measurement of bactericidal activity in body fluids as a clinical research procedure. Laboratory tests used to guide antimicrobial therapy. A simple micro agar diffusion method for the determination of antibiotic concentrations in blood and other body fluids.
Antimicrobial levels and renal function for most antimicrobial agents renal excretion is the major pathway for elimination from the. However detailed studies of concentrations in tissue and pharmacokinetics are lacking. The measurement of antibiotic concentrations in various fluids has been a prominent aspect of the evaluation of new antibiotics and the quality control of their manufacture. Drutz from the division of infectious diseases department of medicine university of texas health science center san antonio texas interpretation of in vitro susceptibility data for antifungal drugs is hindered by the ab. Accurate measurement of serum concentrations of antimicrobial agents is important when the margin between therapeutic and toxic levels is narrow. Pharmacokinetic studies of antimicrobial therapy relate the administration of the drug to the concentration time profile within body fluids and include its absorption distribution metabolism and excretion properties.
For the other body fluids listed the subjects were generally hospitalized patients table 2. With the availability of rapid accurate assays the measurement of antibiotic material in serum and other body fluids is feasible desirable and widely practiced for these purposes. Laboratory tests that can be helpful in guiding antimicrobial therapy include antimicrobial susceptibility testing determination of bacterial beta lactamase production assay of serum inhibitory and bactericidal activity and assay of specific antibiotic levels in serum. In vitro antifungal susceptibility testing and measurement of levels of antifungal agents in body fluids david j. In human subjects concentrations of drug in body fluids have been reported 4 7 9 11 12. Finally because various body tissues bind antimicrobial agents with different capacities 39 and tissue fluidantibiotic concentration is a combination of bound and unbound drug 40 it is necessary to know the protein binding of an antibiotic to both the tissue or body fluid and plasma or serum in order to interpret correctly the significance of the tissue concentration.
The values given for serum and urine were obtained from normal adults in controlled phar macologic studies table 1. Chisholm gd waterworth pm calnan js garrod lp.
Random Post
- aaliyah jay body measurements
- maryse ouellet body measurement
- arjun bijlani body measurement
- body measurements en francais
- milla jovovich body measurements
- body measurement icon
- body labs measurement
- jung so min body measurement
- body fat measurement nottingham
- body measurement kvm
- what are bra measurement
- body measurement tracking chart pdf
- bridgit mendler body measurement
- rachana banerjee body measurement
- body measurement software free download
- girth measurement body fat percentage
- body measurements words
- body measurement fyp
- see your body measurements
- lizzy greene body measurement
- virtual body measurement app
- body measurement template for weight loss
- gwyneth paltrow body measurement
- bra measurement glasgow
- knee body measurement
- body measurements using computer vision
- garima chaurasia body measurements
- body fat measurement device
- bra size for 16 year old
- bra measurement store
- body measurement sewing
- princess mae body measurements
- how does body measurements work
- work out body shape from measurements
- sara sampaio body measurements
- sanne vloet body measurement
- sanjay dutt body measurement
- body measurement of nora fatehi
- camila body measurements
- yasmeen ghauri body measurement
- body measurements wikipedia
- jessica dhillon body measurement
- what does body width measurement mean
- dascha polanco body measurement
- online body measurement
- impedance measurement body fat
- sue ramirez body measurement
- moushumi hamid body measurement
- free inbody measurement
- large size body measurements