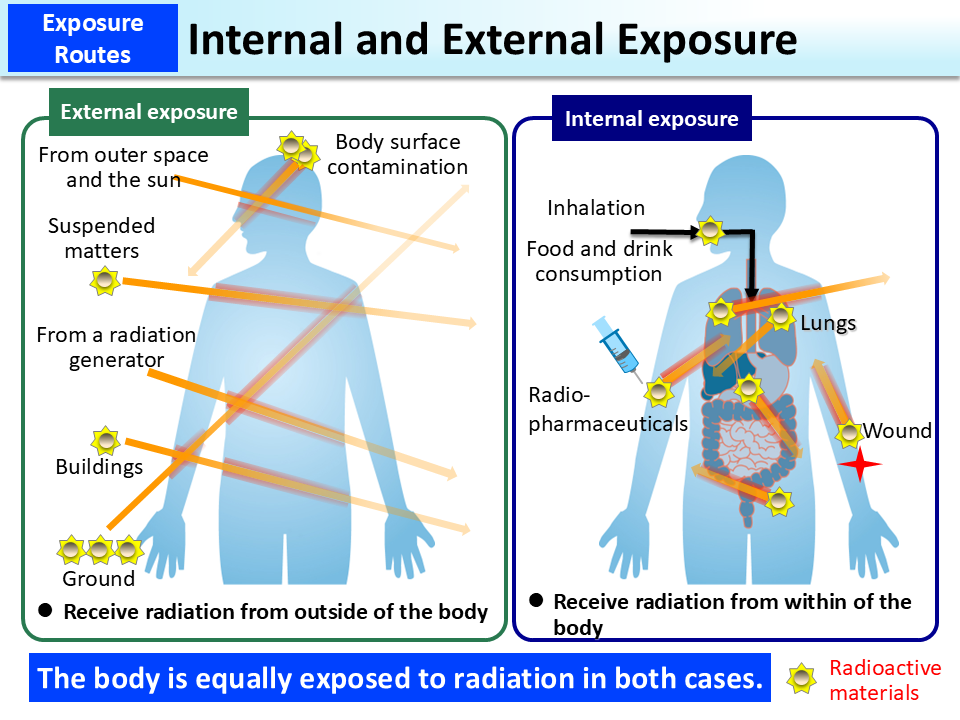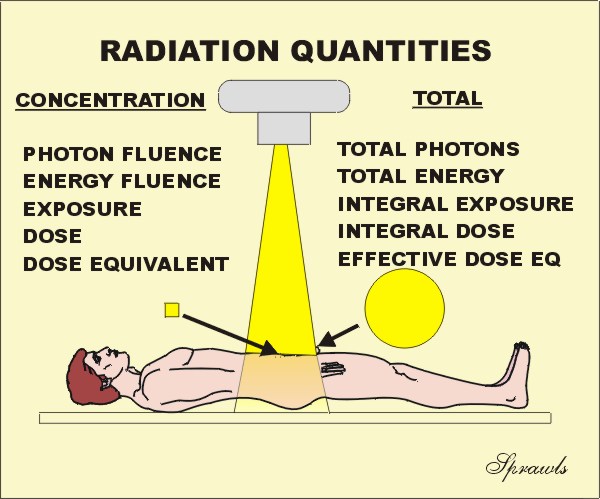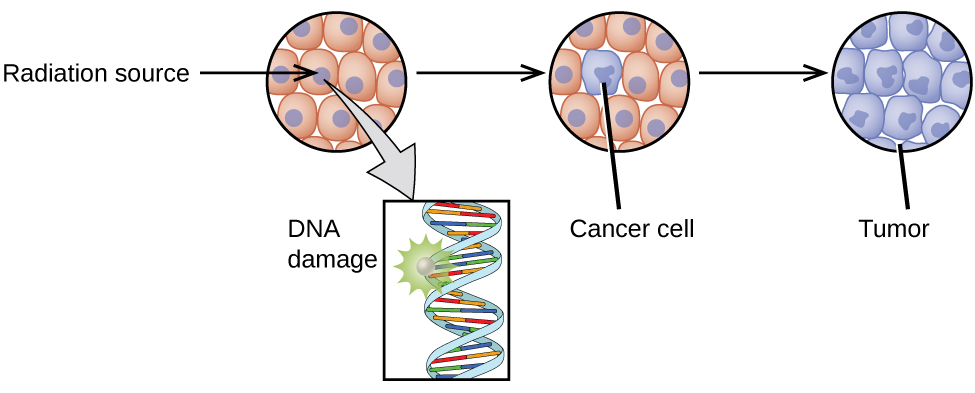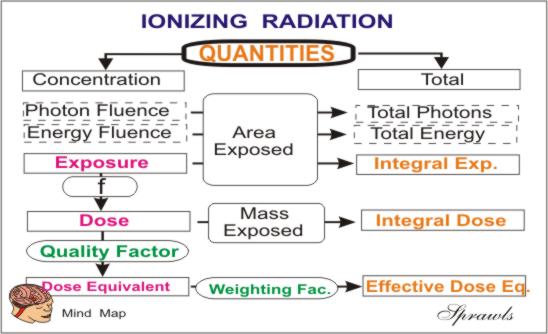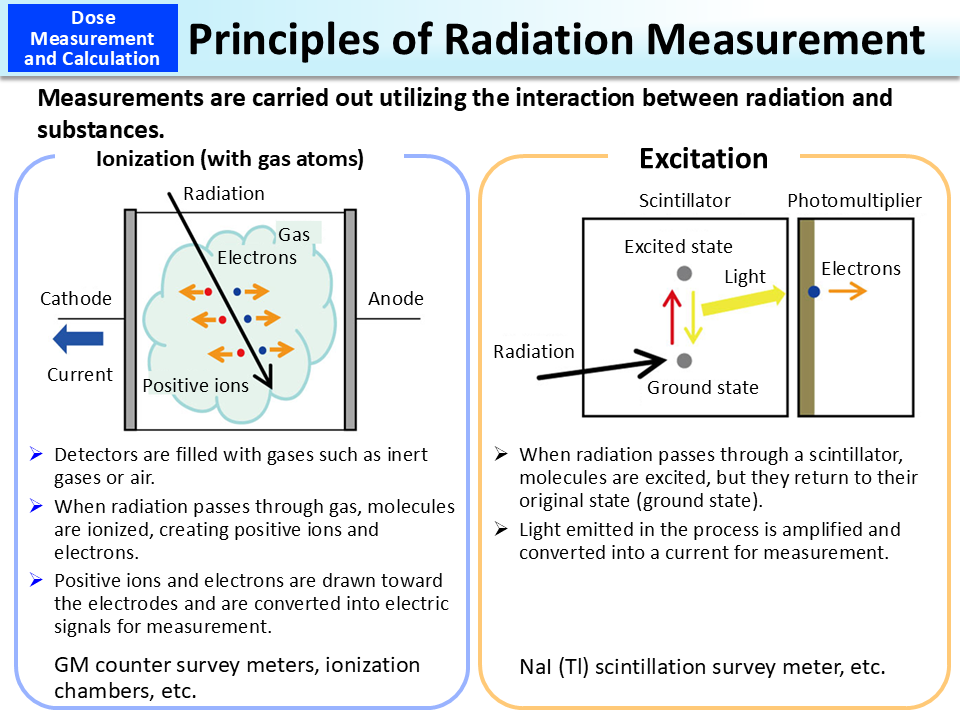
Body Radioactivity Measurement
The units for exposure are the roentgen r and coulombkilogram ckg. It was originally defined in cgs units in 1953 as the dose causing 100 ergs of energy to be absorbed by one gram of matter. Radiation doses are often calculated in the units of rad short for radiation absorbeddose. Setting the scale is a must for meters with analog. In certain circumstances beta emitters can be measured but with degraded sensitivity. Alpha particle decays can also be detected indirectly by their coincident gamma radiation.
Many radiation monitors measure exposure. A radioactive substance can be selectively taken up by different organs or tissue. Get this from a library. The measurement of body radioactivity. The rad is a unit of absorbed radiation dose defined as 1 rad 001 gy 001 jkg. Papers read at a conference held at leeds on april 16 17 1956.
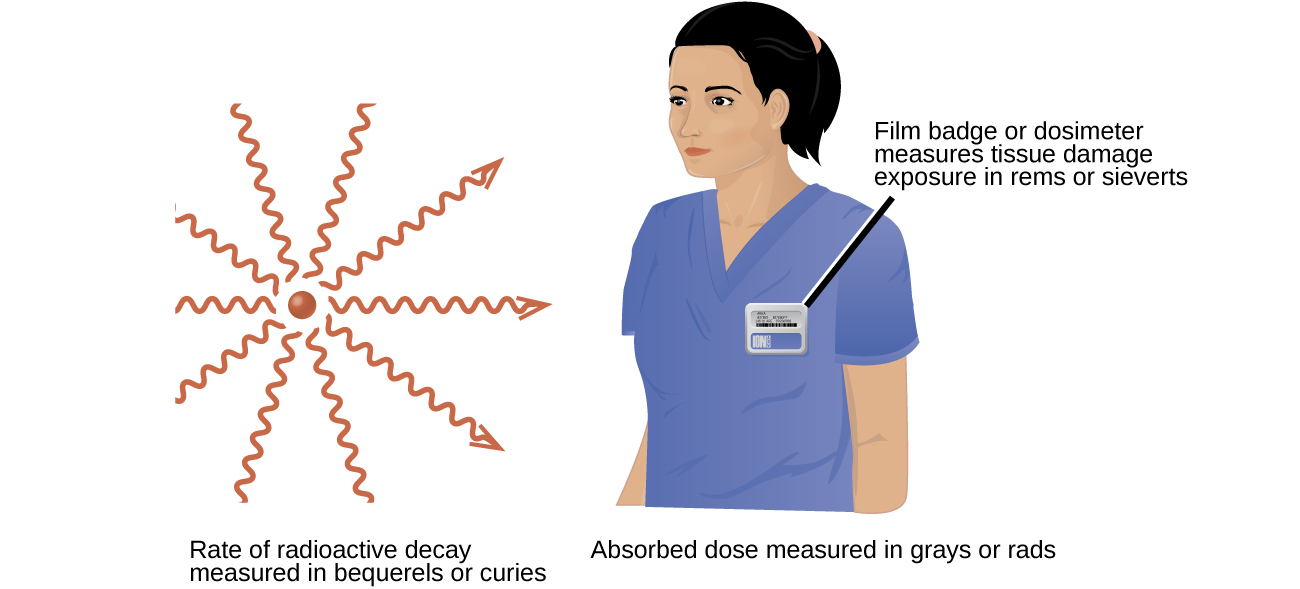
The curie or the becquerel are used as units of measurement when youre looking at how much radiation a material is giving off. National institute of standa. E xposure describes the amount of radiation traveling through the air. If the scale is set to x10 instead of x1 the. It has been replaced by the gray in si derived units but is still used in the united states though strongly discouraged in chapter 52 of style guide for us. This is a count of radioactive incidents regardless of the type of radiation.
Analog devices that measure radioactivity display a scale of counts per minute in intervals of 100. Suppose youre measuring radioactivity and take a reading of 100 cpm. The becquerel is the si unit of radioactive activity and is defined as 1 disintegration per second. British institute of radiology incorporated with the röntgen society. This is defined as the energy imparted to a defined mass of tissue. The units of measure for radioactivity are the curie ci and becquerel bq.
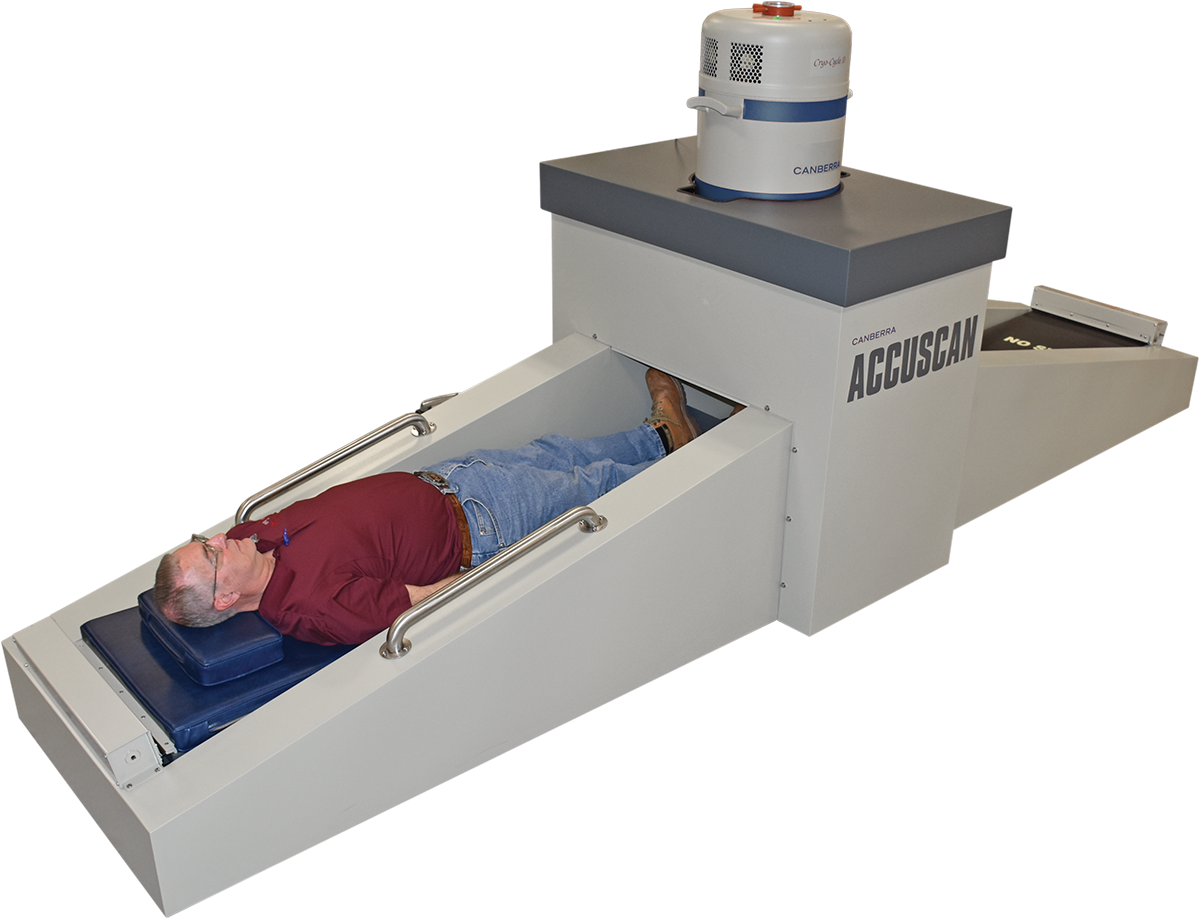
The material absorbing the radiation can be human tissue or silicon microchips or any other medium. The curie ci and the becquerel bq are the units of radioactivity. Dose is generally not uniform over the body. One rad is 100 ergsgram in other words 100 ergs of energy absorbed by one gram of a given body tissue. Measuring radioactive doses dosimetry is the measurement of ionizing radiation in a given place or on a person which is called individual dosimetry. In health physics whole body counting refers to the measurement of radioactivity within the human body.
The radiation dose absorbed by a person that is the amount of energy deposited in human tissue by radiation is measured using the conventional unit rad or the si unit gray gy. The curie is equal to 3710 10 disintegrations per second. The rad or the gray are used to measure radiation a person takes in and the rem or the sievert are used to understand how much risk people have by being around a source of radiation. The biological risk of exposure to radiation is measured using the conventional unit rem or the si unit sievert sv. As a radioprotection tool its purpose is to provide an estimate of quantities such as the equivalent dose or the effective dose resulting from exposure during a certain amount of time. The technique is primarily applicable to radioactive material that emits gamma rays.
Random Post
- kate winslet body measurements
- large bra size measurement
- ashley judd body measurements
- two body measurements that are required when buying jeans
- kofi kingston body measurement
- meryl streep body measurement
- great khali body measurement
- michael b jordan body measurement black panther
- pan xiaoting body measurement
- sakshi dhoni body measurement
- take body measurements
- huma qureshi body measurement
- anna silk body measurement
- body measurement database
- bra size h equivalent
- body fat measurement winnipeg
- khabib body measurements
- body measurement picture
- anna kendrick body measurement
- hempz body measurement
- indian tv actress body measurements
- weight loss body measurement tracker
- hazal kaya body measurements
- body measurement woman
- army selection body measurements
- hania amir body measurement
- anastasiya kvitko body measurement
- body temperature measurement armpit
- taylor cole body measurement
- measurements to figure out body shape
- elisabeth shue body measurements
- one direction body measurements
- rachana banerjee body measurement
- body measurements overweight
- significance of human body measurements in design of equipment
- amanda seyfried body measurement
- sam khan body measurements
- maiza hameed body measurement
- stacy keibler body measurements
- body measurements for kameez
- body measurement tracking iphone
- bhagyashree mote body measurement
- diagram of body measurements
- iso standard body measurements
- loisa andalio body measurement
- body measurements required for miss india
- measurement of body weight length and circumference
- marisa tomei body measurement
- are body measurements in inches
- body fat measurement points